文章插图
07
传播延迟差(SKEW)
SKEW是指在不同的讯号线上,讯号到达接收端的时间差,也就是Delay的差值.
文章插图
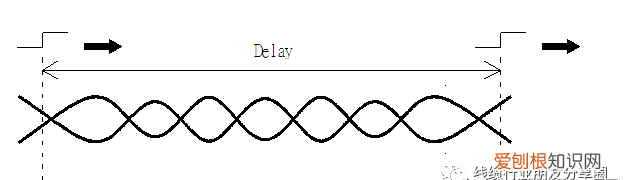
典型的延时差异测试图形
常见的Delay可分为二种:
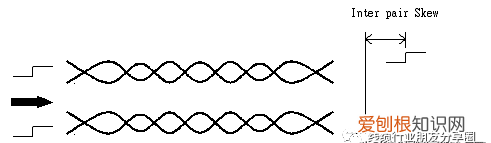
一.差分对内延迟差(Inter-pair Skew),是指输入差分讯号下,同一对线内两导体线之Single-end Delay的差值(相减);是在TDR上设定Differential讯号,一次直接可以量得.
文章插图
二.差分对间延迟差(Inter-pair Skew),是指不同对线间之Differential Delay的差值(相减),(差分)对间延迟差(Inter-pair Skew),是指不同对线间之Differential Delay相减;是分2次以上量测再计算得到的.
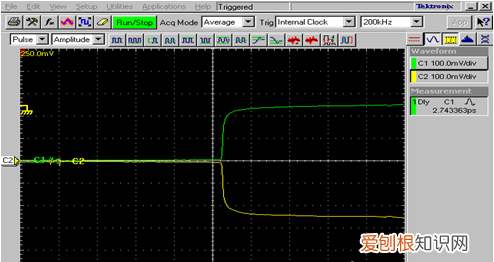
位(时)差-- SKEW 单位:ps/ns
文章插图
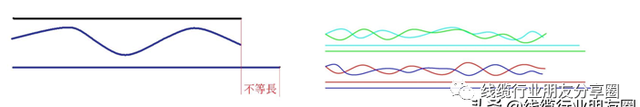
LVDS 是靠+/-一对讯号线在做讯号传输讯号是成双成对的,若其中一根线较长或其他高频效应使讯号跑得不等速,造成讯号在接收端接收的讯号重组时造成还原错误的现象 。
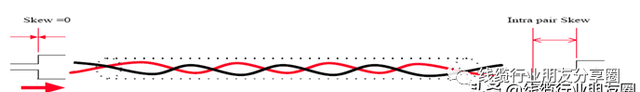
同一对讯号线产生的称Intra Skew
不同对讯号线产生的称Inter Skew
文章插图
关于SKEW
【传播延迟和传输延迟的区别】如果Delay Skew数值越小时,表示讯号传输的时间差越小,线材的传输特性较一致 。反之,Delay Skew数值越大时,表示讯号传输的时间差越多,线材的传输特性较不一致,当差分线对之间不平衡时,就会引入共模噪声 。控制共模噪声的最好方法是使差分线对的两根线尽量在长度上相等、再走线方式上一致、两根线之间的间距尽量保持一致,从而使两根线之间处于平衡状态 。另外,一对差分线中的两根信号线之间的长度不同时,除了会造成skew外,还会在接收端造成抖动,这两点在高频讯号传输的过程中都是要时时注意的,还有一点要注意的是,一个信号线的总长度要尽量避免等于信号波长四分之一的整数倍的情况 。
08
延迟和反射产生的原因
虽然可以达到光速的量级,但毕竟是有限量,随着数字系统时钟频率的不断提高,以至于信号在互连线上传播的时延TD(延迟)与时钟周期相比拟,这时延迟噪声不再能被忽略 。在设计数字系统时序容限时,延迟是最为重要的一环,好在延迟只需要很简单的计算就可以预测到;而反射产生的主要原因是阻抗不匹配,下面我们将SIMON公司整理研究的原文分享给大家,下面的翻译仅供参考!
To several telecommunications professionals, conceptssuch as 'propagation delay' and 'delay skew' bring to mind painful memories ofhigh school physics class. In reality, the effects of delay and delay skew onsignal transmission are easily explained and understood.
Delay is a property that is known to exist for alltypes of transmission media. The propagation delay is equivalent to the amountof time that passes between when a signal is transmitted and when it isreceived on the other end of a cabling channel. The effect is akin to the delayin time between when lightning strikes and thunder is heard-except thatelectrical signals travel much faster than sound. The actual delay value fortwisted-pair cabling is a function of the nominal velocity of propagation(NVP), length and frequency.
NVP varies according to the dielectric materials usedin the cable and is expressed as a percentage of the speed of light. Forexample, most category 5 polyethylene (FRPE) constructions have NVP ranges from0.65c to 0.70c (where "c" represents thespeed of light ~3 x 108 m/s) whenmeasured on finished cable. Teflon (FEP) cable constructions range from 0.69c to 0.73c, whereas cables made of PVC are in the 0.60c to 0.64c range.
推荐阅读
- 联动云租车怎么注册,联动云共享汽车怎么开后备箱
- 瑞纳大灯一般多大功率,瑞纳203款三厢大灯是多少瓦的呢
- 在研招网怎么查拟录取,研究生拟录取怎么查询
- 五月份钓鱼用什么味饵料,五月份钓鲤鱼用什么饵料最好
- 我的世界如何让动物繁殖,我的世界牛怎么繁殖下一代
- 光遇欧若拉钢琴谱,光遇季节任务怎么做
- 小怪兽日记是本书吗,小怪兽日记经典语句
- ivms4200怎么回放录像,海康威视怎么查看回放多少天
- 怎么查学位证书编号,学位证书的编号在哪里可以查到