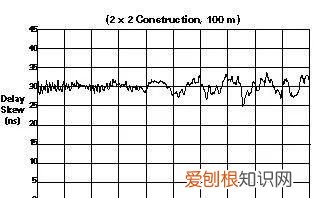
Under some conditions, mixed dielectric constructionsmay even be used to offset delay skew differences that result from differenttwist rates. Figures 1 and 2 illustrate representative delay and skew valuesobtained from a randomly selected 100 meter cable sample having a "2 by2" (FRPE/FEP) construction. Note that the maximum propagation delay anddelay skew for this sample are 511 ns/100m and 34 ns, respectively in the frequency rangefrom 1 MHz to 100 MHz

文章插图
Fig. 1: Cable Propagation Delay
文章插图
Fig. 2: Cable Delay Skew
Now that the issue of delay skew has been brought tolight, cabling system providers are taking great pains to ensure that theirproducts will not contribute to delay skew problems in the field. Manyinstallers ask: "What about my previously installed cabling?" Basedon the fact that the Siemon Cabling System has only approved qualified cablemanufacturers with the most advanced technical competence and manufacturingtechnology, we are able to provide full assurance that the channel requirementsspecified by all cat. 3, 4 and 5 signaling applications for delay and delayskew are met by all existing and new Siemon Cabling System installationscovered by our 16 year application and component warranty.
Regarding future standards developments on the issuesof delay and delay skew, The Siemon Company and its Cable Partners are fullycommitted to providing telecommunications cabling solutions that meet or exceedapplicable standards requirements.
传输延迟是所有类型的传输媒体都存在的一种特性。传输延迟等于信号从线缆信道的一端发送在另一端接收所经过的传输时间 。这就像先看到闪电后听到雷声这其中的时间差,只不过电信号传播得比声音快得多 。对于双绞线来说,实际的传输延迟值是由相速度,线缆长度和频率决定的 。
相速度的变化与线缆的绝缘材料有关 。我们用光速的百分比来表示 。例如:大部分的CAT5结构的速度变化范围是从0.65c到0.70c(c代表光在真空中的传播速度3×108m/s)铁氟龙(FEP)线缆的结构可以达到0.69c到0.73c,而PVC材质只有0.60c到0.64c的范围
对于一段长度一定的线缆来说,低相速度值将会引起额外的延迟 。就像增加线缆端到端的长度就会增加相应的延迟 。和其它很多传输参数一样,延迟是由频率决定的 。
当多线对在同一个线缆显示不同的延迟特性的结果就是延迟差异 。延迟差异是由测量线对间的最小延迟和最大延迟的差值来表征的 。影响延迟差异特性的因素包括材质的选择,比如导体绝缘,物理设计,比如线对捻入率的差异 。
传输延迟和延迟差异是由一些局域网标准制定的标准,测量在最坏情况下100米信道结构特性,来保证信号正确无误地传输 。传输延迟和延迟差异增大所带来的传输问题包括抖动和误码率的增加 。
基于IEEE 802系列局域网规范,TIA正在考虑四线对的三类,四类和五类网络线在1MHz时的最高传输延迟为570 ns/100m,频率高达100MHz时最大延迟差异为45ns/100m 。TIA工作组TR41.8.1也在考虑发展要求,以评估基于ANSI/TIA/EIA-568-A的100欧姆横向链路和信道的传播延迟和延迟差异 。由于TIA委员会的TR-41:94-4 (PN-3772)投票,决定在1999年九月发起对之前颁发的修正草案进行工业投票 。为了反映要求测试的传输延迟和延迟差异有额外要求的线缆和没有要求的线缆的差别,是否改变类别名称(比如cat5.1),这仍旧是一个悬而未决的问题 。
虽然传输延迟和延迟差异正在引起关注,但对大部分LAN应用来说,最重要的关于线缆方面的要求还是衰减串扰比(ACR) 。然而衰减串扰比的差值能提高信噪比,这样就能减少误码率的发生,系统性能是不直接受明显的线缆信道延迟差异值影响的 。例如,对于一个容许延迟差异高达50ns的系统来说,15ns的延迟差异与45ns的延迟差异相比,线缆信道并不会有好的网络特性
推荐阅读
- 联动云租车怎么注册,联动云共享汽车怎么开后备箱
- 瑞纳大灯一般多大功率,瑞纳203款三厢大灯是多少瓦的呢
- 在研招网怎么查拟录取,研究生拟录取怎么查询
- 五月份钓鱼用什么味饵料,五月份钓鲤鱼用什么饵料最好
- 我的世界如何让动物繁殖,我的世界牛怎么繁殖下一代
- 光遇欧若拉钢琴谱,光遇季节任务怎么做
- 小怪兽日记是本书吗,小怪兽日记经典语句
- ivms4200怎么回放录像,海康威视怎么查看回放多少天
- 怎么查学位证书编号,学位证书的编号在哪里可以查到